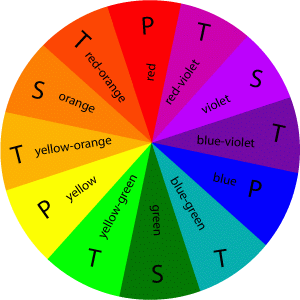
- A color circle, based on red, yellow and blue, is traditional in the field of art.
- Sir Isaac Newton developed the first circular diagram of colors in 1666. Since then scientists and artists have studied and designed numerous variations of this concept.
- Differences of opinion about the validity of one format over another continue to provoke debate. In reality, any color circle or color wheel which presents a logically arranged sequence of pure hues has merit.
The Color Wheel (Primary Colors)
- These are the 3 pigment colors that can not be mixed or formed by any combination of other colors.
- All other colors are derived from these 3 hues.
- These are the colors formed by mixing the primary colors.
- These are the colors formed by mixing a primary and a secondary color.
- A monochromatic color scheme consists of different values (tints, shades, and tones) of one single color.
- Different shades, tones and tints of the same color can be used to give the impression of different colors and provide variety and interest.
- A single color is considered unified, peaceful and harmonious.
- Single colors are effective for establishing an overall mood and tying things together but are considered dull because of the lack of color variation.
Analogous (side-by-side) combinations
- The analogous combination are any 3 colors that are side-by side (adjacent) on the color wheel.
- One color is often a dominant color while the other is an accent color (used for emphasis).
- The wide selection of possible combinations makes this a versatile scheme to use. For example: A selection of purples and blues or oranges and reds can be used to create this scheme
- The similarity of the related colors makes the scheme harmonious. However, the use of more than three colors can dilute the overall effect on this scheme
- These are all analogous color combination schemes:
(Secondary Colors)
- Or a range of cool colors falling between blue and green:
BLUE + BLUE GREEN + GREEN
(Primary + Tertiary + Secondary)
- Analogous colors are any three colors which are side by side on a 12 part color wheel, such as yellow-green, yellow, and yellow-orange.
- Usually one of the three colors predominates.
- The term contrast refers to the degree of difference between tones in an image.
- Contrast can be used to enliven a picture through the use of complementary contrasts such as warm and cool contrasts, or the differences in hue or color saturation.
- When you have too much contrast, all subtlety between the colors is removed giving a 'day-glow' tone.
- If there is not enough contrast, all the colors appear washed out and faded.
- A complete lack of contrast will turn an image completely Grey.
- Color selection is a very important element that affects people emotionally and mentally on the subconscious level.
- Human emotion can detect the effects of cool or warm colors evoking a sense of cool, tranquil relief with blues and greens or the excitement of red and orange.
- Color has a long association with symbolism and affects us psychologically e.g. "seeing red" as associated with anger, being "green" with envy, or perhaps feeling a little "blue”.
- Within each of the colors available, there are limitless variations of hues and intensity.
- It can take a lifetime to understand the subtle distinctions among color ranges, but just knowing the general meaning of each color will help you choose the color thrust for the market you are intending to reach.
RED
- A warm powerful and attention getting color.
- Red is a very visually empowering and attractive color for an e-book cover.
- The color red is extremely dominating.
- Studies show that red can have a physical effect, increasing the rate of respiration and raising blood pressure.
- Use the red color to grab attention and to get people to take action.
- Use red when you don't want to sink into the background.
- Use red to suggest speed combined with confidence and perhaps even a dash of danger.
- When red is highlighted with white we have pink, which is the softer side of red.
- Words associated with this market include:
- Romance, charm, beauty, sweetness, feminine, delicacy, refinement, calming, nurture, security, warmth, tenderness, intuitive, refined, sophisticated, well-bred, reserved, calm, even-keeled, non-violent.
- People who like pink have similar personalities of reds but more subdued (reduced or low in intensity). They tend to be romantic and take care of those around them in a sensitive way.
- Soft, medium tints do not evoke much emotion - many people are indifferent to pink. It is sweetness, innocence, and uncomplicated emotions.
- Orange is the most stable and reassuring of the earth tones
- A combination of red, which commands action, and yellow which adds happiness making this a pleasant warm color.
- As a warm color, orange is a stimulant –stimulating the emotions and even the appetite.
- Because orange is also a citrus color, it can conjure up thoughts of vitamin C and good health.
- Orange is mentally stimulating as well as sociable.
- Use it to get people thinking or to get them talking.
- Pure yellow produces sensations of brightness and warmth reminding us of warm, sunny days.
- Yellow is the second most visually attractive color after red.
- Although it can work as the primary color, yellow often works best as a companion to other colors.
- Use bright yellow to create excitement when red or orange may be too strong or too dark.
- Yellow and blue are a high contrast, eye-popping combination.
- Mix yellow with neutral gray and a dash of black for a high-tech look.
- In Asia yellow is sacred, and imperial.
GREEN
- Green is a combination of blue and yellow.
- The blue qualities represent peace and tranquility, while yellow brings happiness and light hearted feelings to this color.
- Green is a strong color ranging from soft sage and willow, rich jade green, deep forest green and others.
- The new greens communicate peace and growth to your market and is considered a fresh, clean and revitalizing color that speaks of ecology and nature.
- In China, green hats mean a man's wife is cheating on him.
- In France, studies have indicated green is not a good color choice for packaging.
- In India green is the color of Islam.
BLUE
- Listed as the most popular color being the most preferred color universally.
- It is considered to be a "safe" color to use.
- Blue is one of the most calming colors and is often associated with the sky and the sea and evokes peaceful feelings.
- It is regarded as therapeutic to the mind and body.
- Blue can "slow the pulse rate, lower body temperature, and reduce appetite.“
- Blue is considered a business color because it reflects reliability.
- Words associated with this color include:
- Trust, wisdom, tranquility, confidence, conservatism, reliability, belonging, coolness, quiet, truth, seriousness, harmony, serenity, patience, perseverance, peace, intelligence, unity, reassurance, trust, security, hope, generosity, cleanliness, order, sky, water, cold, technology, depression and loyalty.
WHITE
- White represents life and marriage in western cultures, but represents death in the Chinese culture.
- Words associated with this color include:
- Cleanliness, purity, virginal, youth, simplicity, clean, immaculate, fresh, bright, peace, humility, precision, innocence, birth, winter, snow, good, cold, sterile, mild and spirituality.
- People who prefer white tend to be neat and immaculate in their clothing and homes.
- White lovers are inclined to be cautious buyers and shrewd business people, but are critical and fussy.
- White can signify a self-sufficient person and occasionally the innocence and recall of youth and simplistic way of life.
- People who dislike white are usually not very fussy.
- They do not need to have everything placed in an orderly straight line. They are easy going characters and not very uptight about life in general.
Black
- People who like black may be conventional, conservative and serious, or they may think of themselves as sophisticated, or as being very dignified.
- Black lovers tend to feel uncomfortable with the super-sophisticated and feel insecure in their company. They like real people and are not usually dazzled by dignitaries.
- People who hate black sometimes were frightened of the dark during childhood. That experience could be buried in the subconscious in the darkest recesses of the mind and may still haunt them when they look at anything black.
- Black may be simply too heavy and depressing for some people to handle at this point in their lives.
- The reason that primary color combinations tend to not work is because both are high intensity colors, and so side-by-side they appear to vibrate.
- The eye cannot make the adjustment where the two colors meet, making this combination very hard on the eyes.
- This color combination can be used very successfully if you use shades or tints of one of the colors, for instance bright red and navy blue.
- Dark colors, especially dark colored text, on a dark background are very difficult to see
Although a lot of people try to use this combination, it is very difficult to read